Fundamentals
A) Network Components
Clients
Devices that Users access the network with
These can be any device that simply connects network:
- Workstations
- Laptops
- Tablets
- Smartphones
- Smart TVs
Servers
Provides resources to the network Common examples:
- Email Servers
- Files Servers
- Web Servers
- HoneyPots
These servers can be any dedicated hardwares, or within system with help of containerization
Hubs
Older network devices that connect other devices like clients and servers over a local area network.
Hubs have limitations such as increased network errors due to their broadcasting nature.
Hubs —> Bridges —> Switches
Switches
“Smarter hubs” that provide more security and more efficient bandwidth utilization. It delivers from one Port to only destination port, and this helps to prevent unwanted broadcast of data.
Wireless Access Points (WAPs/APs)
Allow wireless devices to connect to a wired network. It works like Hub but using Radio Frequency(RF) Waves.
Routers
Used to connect different networks together. Router can make intelligent forwarding decisions basedon IP addresses of the different clients, servers or other devices.
Modern Routers are predominantly going to rely on the internet protocol to route the traffic across the network using different routing protocols.
Firewalls
Security barriers between internal networks and the Internet. Controls Incoming and Outgoing data flow based upon predetermined security rules by using access control lists. These firewalls can be Hardware based, Software based, or Combination of both.
Load Balancers
Devices or software that distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers. This is going to prevent any one of servers to become Bottleneck, this increases efficiency, capacity, and reliability of services, improving overall network performance.
Proxies
Acts as an intermediary between a user’s device and the Internet. Functionalities:
- Web filtering
- Shared Network Connections
- Data Caching
- Enhanced Security and Privacy
Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems(IDS/IPS)
IDS: Detect unauthorized access or anomalies and alert administrators IPS: Not only detect threats, but also take action to prevent intrusion
Controllers
In Software-Defined Networking(SDN) context, these are central units used to manages flow control to networking devices.
Network-attached Storage(NAS) Devices
Dedicated file storage system that provides data access to heterogeneous group of clients.
Storage Area Network(SAN)
High-Speed network that provides access to consolidated block-level data storage.
Media
In networking,, it refers to the physical materials used to transmit data.
Wide Area Network(WAN) Link
Used to connect networks over large geographical areas.
B) Network Resources
when we talked about network resources, we need to think about how data moved around the network. And we break them into 2 models: Client/Server Model & Peer-to-Peer Model.
Client/Server Model
Utilizes a dedicated server to provide access to network resources (files, scanners, printers, etc.)
-
Easy Administration & Backup
-
Better Scalability
-
Costs More
-
Requires Dedicated OS
-
Requires Specialized Skillset
Peer-to-Peer Model
Peers or other machines (e.g., laptops, desktops) can share resources together directly.
Example for Peer-to-Peer is torrent.
-
Lower Cost
-
No Specialized OS
-
No Dedicated Resources
-
Decentralized Management
-
Inefficient for Large Networks
-
Poor Scalability
C) Network Geography
We divide networks according to their area of coverage.
Personal Area Network(PAN/WPAN)
Smallest type of wired or wireless network which usually covers a distance about 10m or less.
Local Area Network(LAN/WLAN)
Connects components in a limited distance, generally up to about 100m.
Campus Area Network(CAN)
A building-centric LAN that is spread across numerous buildings in a certain area.
Metropolitan Area Network(MAN)
Connects locations that are scattered across the city.
Wide Area Network(WAN)
Connects geographically disparate internal networks.
D) Network Topology
Refers to the arrangement of different elements like links, nodes, clients, and servers that make up a computer network. It is crucial to know these topologies in order to design decent network infrastructure. And Network topology diagram divided into Physical/Logical Topologies.
Physical Topology
Used to show how the network devices and components are physically cabled and connected together.
Logical Topology
Talks about how the traffic is actually going to flow in the network.
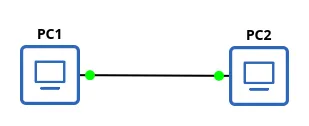
Point-to-Point topology
Simplest form of network topology that involves a direct connection between two devices.
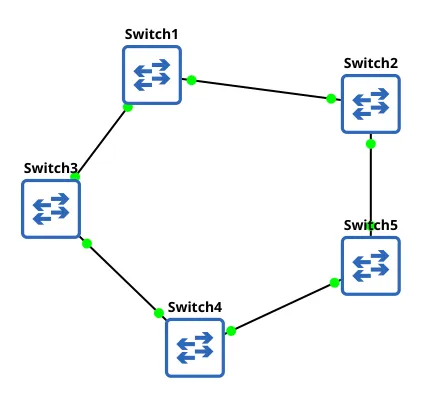
Ring Topology
A network configuration where each devices is connected to 2 other devices, forming a circular data path.
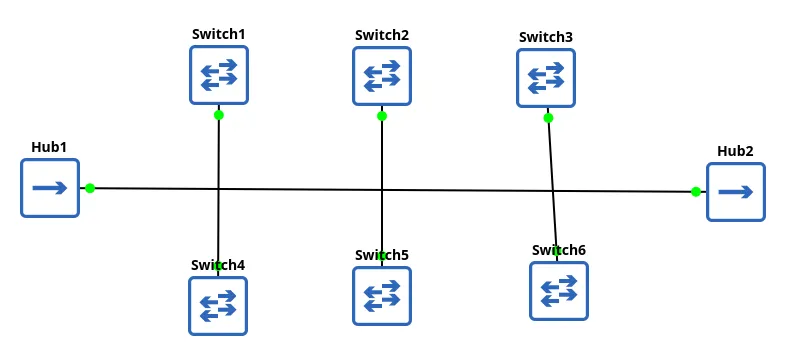
Bus Topology
All of the network devices are connected to a single central cable, called the bus or backbone.
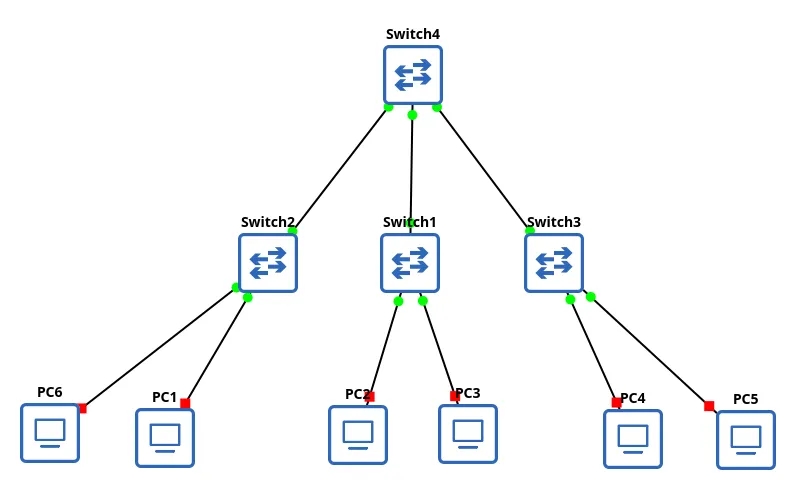
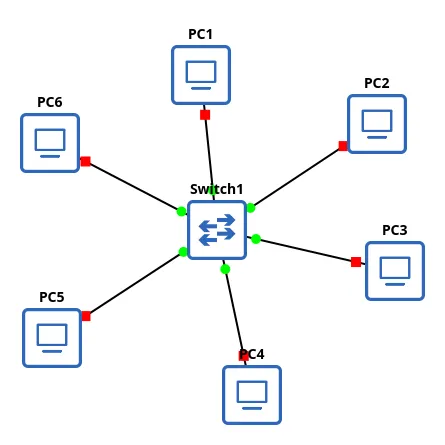
Star Topology
One of the most common network layouts that is in use today
Mesh Topology
Features a point-to-point connection between every single devices on the network to create a robust and redundant network. Full Mesh Formula for Number of Connections:
x = n(n-1)/2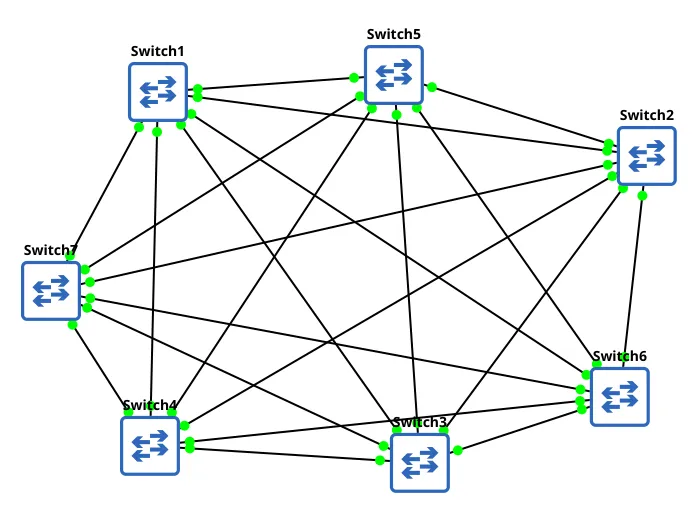
Tree Topology